Contract Farming 🤝 Innovation

Contract Farming is not a new concept. In fact, one of the earliest examples of contract farming can be traced back to ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia.
Farmers entered into agreements with landowners or temples to cultivate land in exchange for a share of the harvest.
These agreements ensured a stable food supply for the community and a regular income for the farmers.
During the 19th and early 20th centuries, contract farming expanded further in response to the increasing demand for agricultural commodities in the industrialized world.
Large agricultural corporations and trading companies entered into contracts with farmers in developing countries to produce raw materials for export.
These contracts often favored the companies, leading to exploitative practices and unequal power dynamics between the parties involved.
In the mid-20th century though, the concept of contract farming evolved with the emergence of agricultural cooperatives and food processing companies.
🚀 Contract Farming is Evolving 🚀
See how?Contract farming has seen various innovations aimed at improving efficiency, maximizing profitability and monitoring sustainability. These are mainly:
Digital Platforms and Mobile Applications:
These platforms connect farmers with buyers, facilitate contract management, provide market information, and offer tools for data collection and analysis.
They streamline communication, enable real-time monitoring of farming activities, and enhance transparency in transactions, benefiting both farmers and buyers.
Smart Farming Technologies:
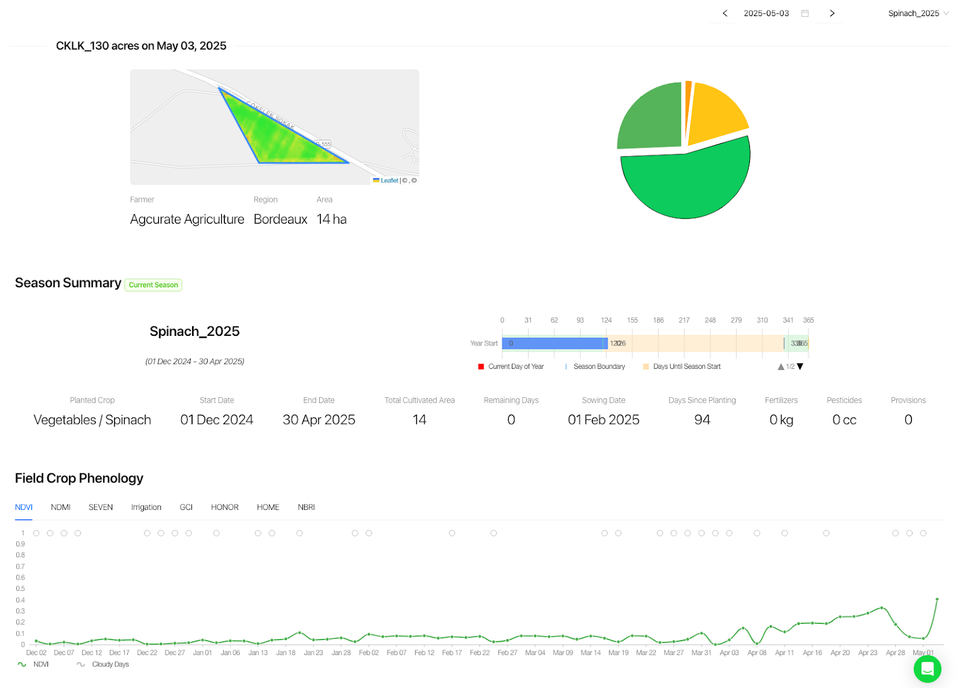
Smart farming technologies, such as remote sensing, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and precision agriculture tools, are being integrated into contract farming practices.
These technologies enable real-time monitoring of crop conditions, soil moisture levels, pest outbreaks, and yield predictions.
Climate Resilient Contract Farming:
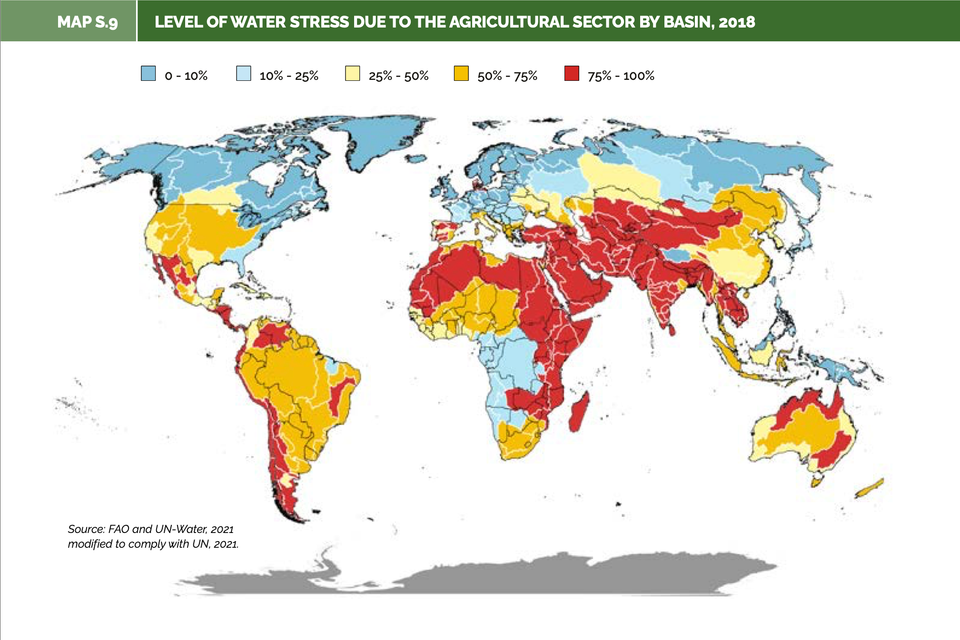
In response to climate change challenges, contract farming has started incorporating climate-smart agriculture practices.
These practices focus on climate adaptation and mitigation strategies, such as climate-resilient crop varieties, water management techniques, agroforestry, soil conservation practices and using agri-insurance products.
See how we empower Contract Farming
FieldOps in ActionOther ways innovation changes the Contract Farming globally are:
Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain technology is being explored in contract farming to enhance transparency, improve accountability, reduce fraud, and maintain the integrity of contract farming relationships.
Critical information related to contracts, transactions, quality certifications, and product origins can be recorded and accessed by relevant stakeholders.
Inclusive Contract Farming Models
Innovations in contract farming aim to make the model more inclusive, especially for small-scale farmers and marginalized communities.
Initiatives include creating farmer producer organizations, capacity-building programs, and implementing fair trade and responsible sourcing principles.
These efforts promote fairer contract terms, strengthen farmers' bargaining power, and ensure equitable distribution of benefits.
Ecosystem Services Integration:
Contract farming is increasingly considering the provision of ecosystem services in agriculture.
This involves incorporating sustainable land management practices, biodiversity conservation, and natural resource protection.
Incentivizing farmers via payments for ecosystem services (PES) encourages them to adopt practices that promote biodiversity, protect water sources, and preserve habitats